Business Intelligence Architecture: Elements, Layers, Advantages, & More
Businesses today are well aware of the importance of using data to make informed decisions. This can be confirmed by the fact that 67% of global businesses now have access to business intelligence tools. It shows how invaluable BI has become in modern organizations.
To capitalize on this technology, effective business intelligence architecture must be put into place for successful analysis and reporting. In this blog, we will explain why such an architecture is significant, its elements, advantages, and layers involved.
What is Business Intelligence Architecture?
The framework of technologies used by companies for their business intelligence and analytics requirements is known as a business intelligence architecture. It encompasses various IT systems, data integration procedures, storage programs, and software applications necessary to gather information. This information can be about important company operations and trends reported to inform corporate executives or other users within the organization.
A well-designed BI architecture forms an essential part of any successful BI initiative which seeks to track performance indicators and refine processes. It aims at discovering new earning opportunities through efficient analysis reporting.
Elements of BI Architecture
The following are the three elements of a successful BI architecture.
1. Data Management
These are the processes, techniques, and tools used for collecting, organizing, and storing data. To effectively support business intelligence initiatives, organizations need a comprehensive data management system. This should be designed in such a way that meets the unique needs of the organization and allows for scalability, security, and performance optimization.
Data collection from internal sources, like employees entering information into databases, should be managed. Data from external sources, such as social media feedback or market research firms must also be managed efficiently while remaining compliant with applicable regulations. By doing this, one can ensure reliable access to accurate and up-to-date data, which is essential for successful BI implementations within an organization.
2. Analytics
Data analytics is the practice of utilizing data to gain insights and make informed decisions. It involves turning raw data into actionable intelligence through descriptive, predictive, or prescriptive analysis techniques.
By using these methods, businesses can get a better understanding of their customers’ behavior, operations metrics, and industry trends to remain competitive. With the right use of analytics, it’s possible to uncover patterns that would otherwise go unnoticed.
3. Technology
This includes the various software and hardware tools that businesses use to facilitate their business intelligence projects. These range from data warehouses, extract-transform-load (ETL) systems, reporting platforms, visualization applications, etc.
It also necessitates having people who have technical skills, like database knowledge or coding experience, and can interpret data insights well. On top of that, organizations must invest resources into training programs for employees to learn how best to utilize existing tools while staying current with innovations.
To learn more about business intelligence elements, you can opt for this comprehensive Power BI course.
BI Architecture Layers and Diagram
Deploying a BI architecture can be done either in an on-premises data center or the cloud. Either way, these deployments are made up of core layers that help with collecting, integrating, and storing data for analysis purposes. They also help with visualizing the gathered information and using those results to make strategic business decisions.
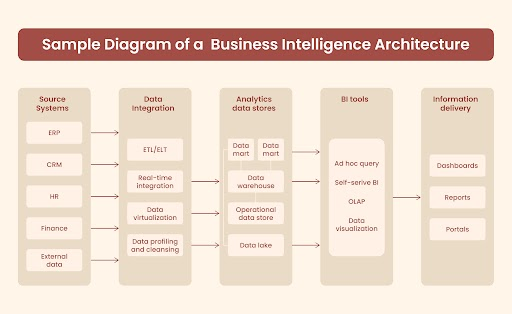
This diagram shows how different areas communicate with one another to provide information for decision-making within the organization. As can be seen in the accompanying BI architecture diagram, there are several business intelligence architecture layers, which include:
1. Source Systems
All the systems that store transactional and operational data necessary for a business intelligence program, such as ERP, CRM finance, manufacturing, and supply chain management systems are called source systems. This includes external sources like market or customer databases from outside providers to get the information needed for an effective BI architecture.
Factors used in selecting these sources include relevance, currency (how outdated it is), quality, and level of detail available in each data set. In addition, structured, semi-structured, or unstructured pieces may be required depending on what type of analysis needs to take place.
2. Data Integration
An organization needs to put together all the different data sets they have collected to properly analyze them through a BI program. A commonly used solution here is ETL (Extract, Transform, and Load) software that can pull data from source systems as part of one batch process.
Other methods, such as real-time integration or virtualization may also be applied depending on specific requirements. Data integration tools help fix any errors before using this information to produce clean and consistent results.
3. Analytics Data Stores
Data storage for business intelligence involves different repositories to store and manage information used in BI. The primary repository is usually a data warehouse that stores structured data, like relational databases or multidimensional formats to make it available for queries and analysis. Organizations might also have individualized departments set up with their own specialized needs known as data marts.
Another temporary option is an operational data store that holds recent transaction records before they go into the main warehouse. This can be on one database server or several separate systems depending on the size of the environment needed. In addition, big/raw data platforms, such as Hadoop clusters are useful too.
4. BI Tools
Companies use different technologies to make sense of their data and show the information in an easy-to-understand way for business users. This could mean using tools, such as ad hoc query, data mining, online analytical processing (OLAP) software, and self-service BI.
These tools give business intelligence analysts the ability to ask questions without needing assistance from dedicated BI teams. Also, they might use visualization technology that includes graphs and charts to display trends within datasets.
5. Information Report Tools
Information delivery tools, such as dashboards, portals, and reports provide business users with the ability to see insights from BI and analytics applications. Data visualization is often available along with self-service functions for further analysis.
For instance, a dashboard or portal can be configured so that real-time data access is provided. It offers different views of information and allows an individual to delve deeper into the figures. Reports usually present data in non-dynamic ways.
Get an assured Job guarantee by enrolling in our data science placement guarantee course.
Advantages of a BI Architecture
Given below are some of the benefits of using BI analytics and how it can revolutionize an organization.
- Coordination
Having proper BI architecture guides teams to coordinate and work in an orderly manner. This helps them to follow standards, guidelines for data management, and analytical approaches, which allows for streamlined development of BI solutions. It also lowers repetition while optimizing overall performance.
- Better Management of Data
It ensures that data within the organization can be handled and managed correctly. This setup helps integrate, assess the quality, and oversee any data collected so that it is precise enough to draw accurate conclusions. It promotes better accuracy, consistency, and dependability when analyzing information, which leads to gaining useful insights.
- Accessibility and Availability of Data
Accessibility ensures that data is easily accessible for those authorized to use it. This includes having processes, such as integration and warehousing, which allow users to quickly retrieve what they need when needed. It helps in decision-making and staying up-to-date with the latest information available.
Disadvantages of BI Architecture
Though BI architecture is advantageous, there are some challenges that organizations face.
- Lack of Resources: Maintenance of BI architecture requires sufficient time, money, and personnel. If an organization lacks these resources, the architecture may become inefficient.
- Implementation Challenges: Implementing a business intelligence architecture can be challenging as it requires varied business strategies, processes, technologies, and systems to align together. It may take a lot of time to see a return on investment.
- Maintenance Issues: The viability of the BI architecture depends on its continuous update and maintenance. Without regular evaluation of BI practices, the system may become redundant and might not be able to cater to the current needs of the organization.
- Measuring Returns: Measuring returns on investment made to establish the architecture is challenging since there are no universal key metrics to analyze them.
- Adaptability Issues: Not all the stakeholders may agree to the changes brought in by the business intelligence architecture and may find it difficult to adapt to new practices, procedures, and organizational roles.


How Do Architectural Layers Differ From Components?
Business intelligence architecture has five layers. These architectural layers contain various components for the entire system to function properly. The five layers of BI architecture with their major components are:
- Data Sources: External or internal sources that provide information for BI systems to work are data sources. They form the first layer of the architecture and have components, such as databases, files, cloud services, etc.
- Data Integration and Quality Management: In this layer, datasets are consolidated and cleaned for analytical purposes. Here, the Extract Transform and Load (ETL) process extracts data from source systems, converts it into a format, and stores it for further operations. Power Query Editor is used to transform data in this layer.
- Data Repositories: This layer consists of repositories that store consolidated data for further processing. It has components, such as data warehouses and data marts.
- BI and Analytics: Here, the data is studied and analyzed to gain meaningful insights for decision-making. It contains components, such as query and reporting tools, data mining tools, AI and ML tools, data visualization tools, and Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) tools.
- Data Governance: This layer ensures data governance standards and policies are followed during the processes in the above four layers for maintaining quality and security. Business glossaries, data catalogs, and data policies are some of the components of this layer.
How to Create an Effective Business Intelligence Architecture?
Here are steps to create an effective business intelligence architecture for your organization.
- Define Objectives: Begin by identifying your organization’s business objectives. Define your key performance indicators, data sources, target users, and expectations. It helps with optimized resource allocation and formulation of efficient strategies.
- Form a Team of Experts: BI experts can help you design an efficient architecture that can be updated with changes in data sources, technology, and organizational requirements.
- Decide a Budget: Once you have a team, compare the costs of implementation and benefits and decide on a sufficient budget.
- Choose BI Tools and Platform: Based on your objectives, expectations, budget, and integration capabilities of current tech, select the best business intelligence tools and platform to form the business intelligence architecture.
- Design BI Architecture: Design your BI architecture with the tools and platform you have selected. Ensure it can handle the data flow, processing, storage, and presentation.
- Implement and Evaluate: Once you have an architecture in place, implement it to test and validate your BI solutions. With continuous evaluation of the architecture, you can measure its performance and implement further improvements.
Strategies for Incorporating Business Intelligence in an Organization
If you are considering implementing business intelligence in your organization, here are some tips that you should keep in mind.
1. Business Intelligence Is Not a One-Time Thing
Business intelligence is an ongoing process rather than a one-time project. To get the most out of it, you need to ensure that it is embedded into your organization’s culture and day-to-day operations.
This can be done by regularly gathering data from sources across the organization; analyzing this information for useful insights, and then using those results to improve processes.
2. Business Intelligence Needs All Hands on Deck
At the senior management level, it is important to ensure a clear understanding of how business intelligence will benefit the organization and employees. It helps if senior executives are able to demonstrate their support by using data in decision-making or leading initiatives based on insights gained from business intelligence systems.
They should understand why investing time into implementing a business intelligence system would help them succeed in achieving desired outcomes, such as improved customer service, increased profits, cost reduction, and so forth.
3. Business Intelligence Does Not Replace Good Decision-Making
Business intelligence can give you access to useful information. However, you should know that business intelligence alone is not the only factor in determining outcomes for your organization. Good decision-making and sound judgment are very important as well.
Therefore, a strong balance between using available information from business intelligence and personal expertise can guarantee success.
4. Business Intelligence Is No One-Size-Fits-All Solution
Business intelligence is a tool used to gather data and analyze it to make informed decisions about how your business operates. It can be an incredibly effective way of finding patterns or trends that have the potential for improving profitability, but not all solutions work for every organization. It is because each company has its unique needs based on size, industry type, complexity of operations, etc.
Conclusion
Developing a great business intelligence architecture is necessary to successfully gather, analyze, and report operational data. This architecture consists of different layers, which can provide the organization with amazing benefits. To ensure an efficient implementation process, stakeholders must be involved at each stage.
What are some of the best practices you will employ to make a BI architecture more efficient? Let us know in the comments section below. Also, check out more technicalities of BI with these top business intelligence tools.
Business intelligence is a set of strategies and technologies including data analytics, data visualization, data mining, etc., used by organizations to make data-driven decisions.
Intelligence architecture is a framework that includes data management, analytics practices, and technology standards that power an organization’s BI process.
The five layers of business intelligence include data sources, data integration and quality management, data repositories, BI and analytics, and data governance.